 |
Application Gallery
| Medicine:
CT and MRI |
    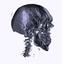 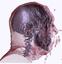 |
| In radiology, tomographic measurement such as computed
tomography (CT) and magnet resonance imaging (MRI) is used to gain
insight into the human body. Direct volume rendering techniques are
appied to visualize the resulting data sets in 3D.
|
| Geology:
Plasticine Models of Folds and Boudins |
 |
| Analoque modeling in structural geology is performed to gain
insight into the deformation process of natural rock and the forces
which are related to it. Throughout these experiments, the
structural geometry of layered rocks is modeled by means of
plasticine models. After tomographics measurement, the spatial
structures inherent in such models are visualized using direct
volume rendering. |
| Medicine:
CT: Middle and Inner Ear |
   |
| With high-resolution spiral-CT scanners, it is possible to
record very tiny anatomical structures, such as the middle and the
inner ear. The analysis of these vulnerable structures is of great
importance for the planning of surgery close to the temporal bone.
|
| Computer
Science: Random Number Generators |
   |
| Dan Kaminsky (doxpara.com) has pointed me to
entropy visualization, an unusual application of direct volume
rendering. The quality of many sequential random number generators
can be evaluated by rendering a basic phase space analysis of their
output. |
|
 Application Gallery Application Gallery
| MaterialsScience:
Microstructures |
 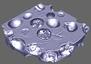  |
| In materials science and enginnering, tomographic measurement
is used to examine the interior of structural components and
composite materials. For the visualization of such data sets direct
volume rendering is essential. |
| History:
Visualization of Archaeological Items |
 |
| For the examination of archaeological items, such as ancient
busts, statuettes and vases, tomographic measurement and direct
volume rendering has proven helpful to visualize internal structures
and to investigate the process of manufacturing.
|
| Medicine:
CT Angiography |
   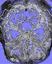  |
| An intracranial aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilatation
of a cerebral artery filled with fluid or clotted blood, resulting
from a disease of the vessel wall. As a result of a weakness of the
different layers of the vessels wall, there is a considerable risk
that a rupture of the aneurysm will lead to severe haemorrhage in
the brain. The term angiography refers to the roentgenographic
visualization of blood vessels after injection of a radiopaque
substance. |
| Geology:
Fossils |

|
| Tomographic measurement and direct volume rendering can be
utilized to reveal spatial structures inside lacustrine limestone,
such as fossils. |
|

 Application Gallery
Application Gallery
